Melanoma prevention and treatment: Protect your skin and your health
Melanoma is a type of Skin Cancer that originates in melanocytes, the cells responsible for skin pigmentation. It is one of the most aggressive and dangerous forms due to its ability to metastasize, so early detection and treatment are essential.
Risk factors
Melanoma occurs when melanocytes become malignant, forming cancerous lesions. It is most common in fair-skinned people, especially those prone to sunburn. However, other factors also increase the risk:
- Excessive sun exposure:Ultraviolet radiation, whether from the sun or tanning beds, is one of the main triggers
- Genetic factors:Some cases are related to inherited genetic mutations
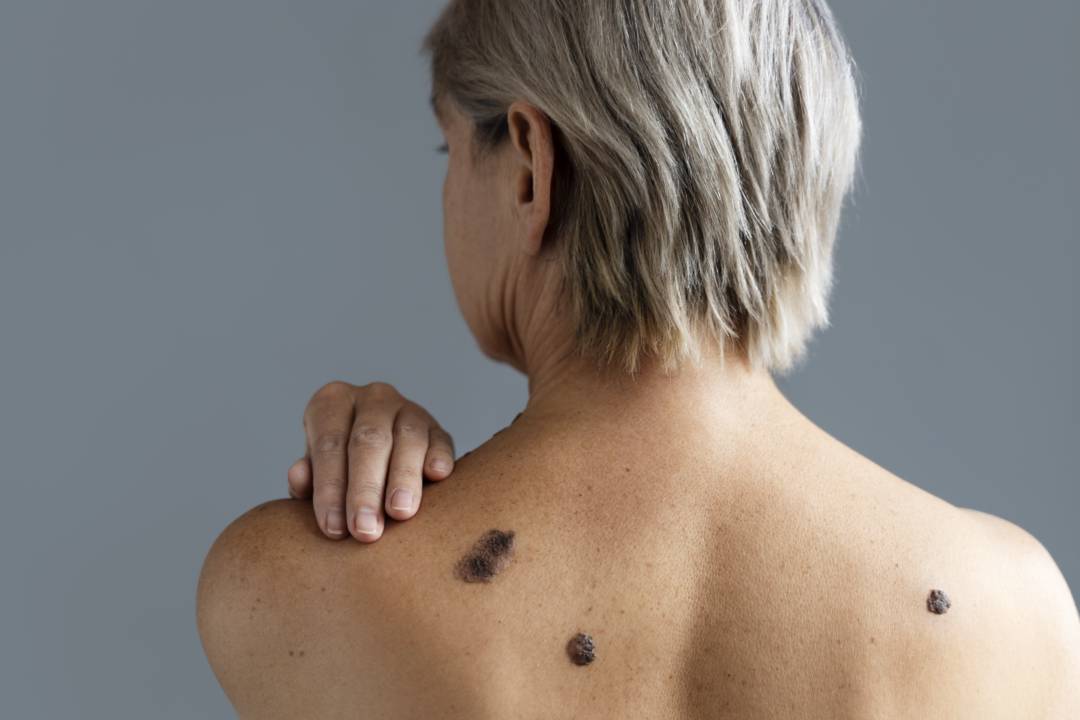
- Presence of Moles:have more than 100 in the body, whether atypical or giant congenital
Types of Melanoma
There are four main types:
- Superficial Spreading Melanoma:It is the most common and usually affects the outer layer of the skin
- Nodular Melanoma:It tends to grow rapidly in depth and is considered one of the most aggressive types
- Acral Lentiginous Melanoma:Frequent in palms, soles of the feet and nails, this subtype is more common in regions such as Colombia and can behave more aggressively
- Lentigo Malignant Melanoma:It usually appears in areas with greater sun damage, such as the face and neck, in older people
Identify a Melanoma: the ABCDE technique
Detecting a melanoma early can make a difference in its prognosis. The ABCDE technique helps to identify suspicious moles:
- A (asymmetry):If one half of the mole is different from the other
- B (edges):irregular, jagged or poorly defined edges
- C (color):varied shades within the same mole, such as brown, black, blue, red or white
- D (diameter):Moles larger than 6 millimeters (similar to the size of a pencil eraser)
- E (evolution):Rapid changes in the size, shape, color, or elevation of the mole
Diagnosis and tools for early detection
Melanoma is initially suspected by clinical evaluation, but should always be confirmed by a skin biopsy. This technique not only confirms the diagnosis, but also determines the degree of invasion and the prognosis of the tumor.
A key complementary tool is Dermoscopy, which allows for the examination of specific characteristics of Moles not visible to the naked eye.
Stages of Melanoma and Available Treatments
Melanoma is classified into four main stages:
Stage 1
- Description: Melanoma is located in the most superficial layers of the skin
- Forecast: excellent
- Treatment: surgical Resection of Tumor
Stage 2
- Description: Melanoma invades deeper layers of the skin, but remains localized
- Forecast: well, although there is a higher risk of metastasis
- Treatment: surgical intervention plus Sentinel Node Biopsy. In some cases, Immunotherapy is considered
Stage 3
- Description: Melanoma invades the lymph nodes near the lesion
- Forecast less favorable, although it has improved with advanced treatments
- Treatment: surgery for the tumor and affected lymph nodes, complemented with immunotherapy or targeted therapies
Stage 4
- Description: Melanoma has spread to distant lymph nodes or other organs
- Forecast: reserved
- Treatment: Immunotherapy, Targeted Therapies, Radiotherapy and, in some cases, experimental studies with Vaccines
Prevention: How to reduce the risk of melanoma
Prevention is key to avoiding this type of cancer. Strategies include:
- Sun protection:Apply sunscreen daily, with a high protection factor, even on cloudy days
- Avoid the sun during critical times:Limit sun exposure between 11 a.m. and 3 p.m.
- Protective clothing:Wear long sleeves, wide-brimmed hats, and UV-protective sunglasses
- Avoid tanning beds:These are associated with a high risk of developing Melanoma
- Self-exploration:Check your skin regularly, including palms, soles and nails, and consult a specialist if any suspicious changes occur.
Importance of education from an early age
It is essential to educate the population, especially children and young people, about the importance of preventing sunburn and adopting healthy habits to protect the skin.
Campaigns in nurseries, schools and universities can have a significant impact on reducing the incidence of Melanoma.
Taking care of your skin is taking care of your life
Melanoma is a potentially fatal skin cancer, but it is preventable and treatable if detected early. With the use of tools such as the ABCDE technique, early diagnosis and access to advanced therapies, it is possible to significantly improve the quality of life of patients.
Prioritising education, avoiding excessive sun exposure and adopting protective measures are essential to reducing the impact of this serious public health problem.
